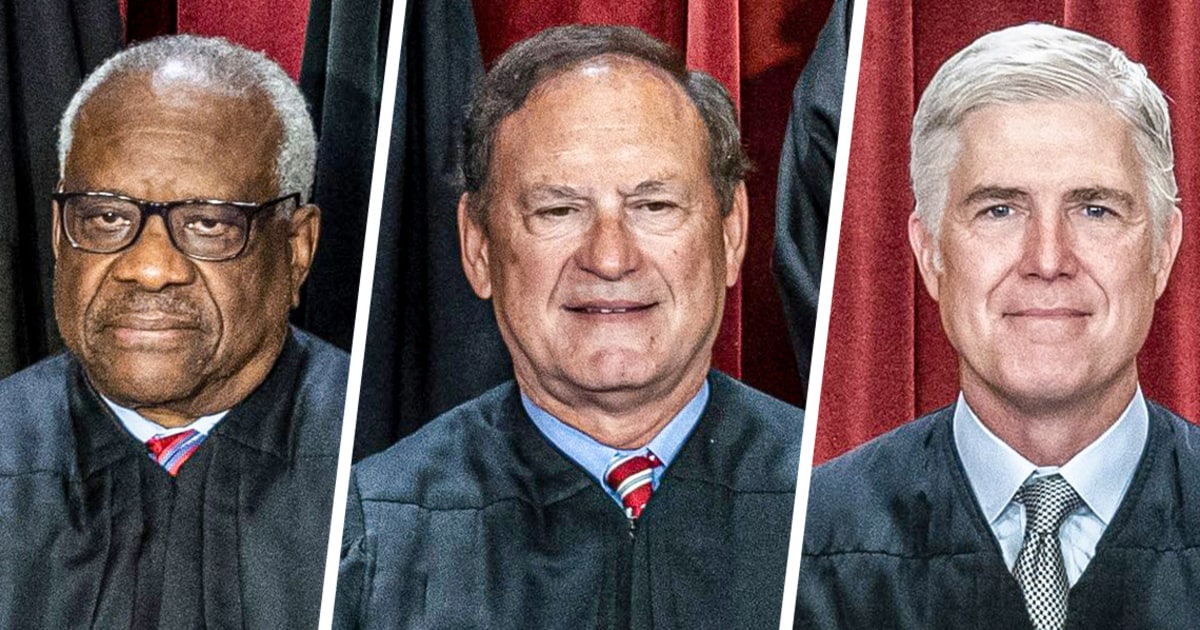
In a recent decision, Supreme Court Justices Clarence Thomas, Samuel Alito, and Neil Gorsuch dissented from the majority’s order to halt an appeals court ruling concerning the Voting Rights Act. This action marks a significant moment in the ongoing legal battles surrounding voting rights in the United States. The dissent raises questions about the future of the Voting Rights Act and its enforcement. Understanding the nuances of this decision and the dissenting opinions is crucial for anyone following legal developments.
This article breaks down the Supreme Court’s order, the dissenting arguments, and what it all means for the future. This includes providing context of the Voting Rights Act itself, and the implications of the 8th Circuit’s unusual stance.
The Supreme Court Halts Appeals Court Ruling
The Supreme Court’s decision to halt the 8th Circuit Court of Appeals ruling provides temporary relief for Native American tribes and individuals who sued over a North Dakota legislative map. This map was challenged under Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act, which prohibits discriminatory voting practices. The court’s action prevents the appeals court ruling from taking effect, ensuring that private parties can continue to use federal law to enforce Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act.
The 8th Circuit’s position, which asserts that private parties cannot use federal law to enforce Section 2, is an outlier compared to other federal appeals courts. This unusual stance prompted the plaintiffs to seek emergency relief from the Supreme Court. The plaintiffs argued that the 8th Circuit’s stance would severely undermine Congress’s most important civil rights statute, particularly affecting Native Americans in North Dakota with a history of discrimination.
Thomas, Alito, and Gorsuch: The Dissenting Voices
Justices Thomas, Alito, and Gorsuch dissented from the court’s decision without providing a detailed explanation, typical of the court’s “shadow docket” proceedings. Their dissent aligns with their past voting records in election-related litigation, where they have often diverged from their colleagues. This consistency suggests a principled disagreement with the majority’s approach to voting rights issues.
Chief Justice John Roberts and Justice Brett Kavanaugh have, in the past, sided with Democratic appointees on voting rights cases. The division within the court underscores the contentious nature of voting rights litigation and the differing judicial philosophies among the justices. This split highlights the challenges in achieving consensus on these critical issues.
Temporary Relief for the Voting Rights Act
The Supreme Court’s temporary halt to the appeals court ruling offers a reprieve for the Voting Rights Act. The act, designed to combat discriminatory voting practices, has faced increasing challenges in recent years. The 8th Circuit’s ruling could have significantly weakened Section 2, making it more difficult for private parties to challenge discriminatory voting laws.
By pausing the 8th Circuit’s decision, the Supreme Court ensures that the Voting Rights Act remains enforceable, at least for now. This decision allows ongoing litigation to proceed under the established understanding of Section 2. However, the temporary nature of the relief means that the Supreme Court could weigh in later with a more restrictive ruling.
The Shadow Docket and Unexplained Decisions
The Supreme Court’s decision was made via the “shadow docket,” meaning it was issued without detailed explanations or oral arguments. This practice has drawn criticism from legal scholars and advocates who argue that it lacks transparency and accountability. The absence of a signed opinion from either the majority or the dissenting justices leaves observers to speculate about the reasoning behind their positions.
The use of the shadow docket in such a significant case underscores the increasing reliance on this mechanism for resolving contentious legal issues. While it allows the court to act quickly, it also raises concerns about the potential for inconsistent or poorly reasoned decisions. The lack of transparency can erode public trust in the judiciary and fuel perceptions of political influence.
State Officials Urge Normal Course
State officials unsuccessfully opposed the pause on the 8th Circuit ruling, arguing that the court should “follow the normal course” and allow the circuit ruling to take effect. This position reflects a broader effort by some states to limit the scope of the Voting Rights Act and assert greater control over election administration. These states argue that federal intervention infringes on their sovereignty and disrupts established procedures.
The state officials’ stance highlights the ongoing tension between federal and state authority over election matters. The Supreme Court’s decision to grant temporary relief suggests a reluctance to cede too much ground to state control, particularly in cases involving potential discrimination. However, the court’s ultimate ruling could still shift the balance of power in favor of the states.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Voting Rights
The Supreme Court’s decision to temporarily halt the 8th Circuit ruling provides a brief respite for the Voting Rights Act, but the underlying issues remain unresolved. The dissenting opinions of Justices Thomas, Alito, and Gorsuch signal a continued willingness to challenge the established understanding of the act. The court’s ultimate ruling in this case could have far-reaching implications for voting rights across the country.
The battle over voting rights is likely to continue, with ongoing litigation and legislative efforts aimed at either expanding or restricting access to the ballot box. The Supreme Court will play a central role in shaping the legal landscape, and its decisions will have a profound impact on the future of American democracy. Monitoring these developments and understanding the legal arguments involved is essential for informed citizenship.
Leave a Reply